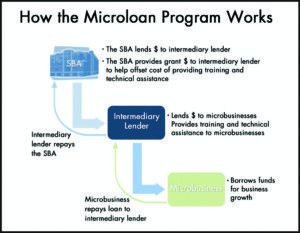
How does a microloan work?
A microloan is a financial tool designed to provide small amounts of capital to individuals or small businesses who may not have access to traditional forms of financing. It is a type of loan that has gained popularity in recent years, particularly in developing countries, as a means to alleviate poverty and promote entrepreneurship.
Unlike traditional bank loans, microloans are typically offered by microfinance institutions (MFIs), which are specialized financial institutions that focus on serving low-income individuals and communities. These loans are characterized by their small loan amounts, often ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars, and their simplified application processes.
Microloans are often provided to borrowers who lack collateral or a credit history, making them more accessible to those who are typically excluded from formal financial systems. Instead of relying on traditional credit scoring methods, MFIs assess borrowers based on their character, business plans, and potential for repayment. This approach allows individuals with limited financial resources to access the capital they need to start or expand their businesses.
One of the key features of microloans is their short repayment terms. Unlike long-term loans, microloans are designed to be repaid within a relatively short period, usually ranging from a few months to a couple of years. This shorter repayment term reduces the overall risk for both the lender and the borrower and ensures a faster turnover of funds, allowing MFIs to recycle the capital and support more borrowers.
Interest rates on microloans are generally higher compared to traditional loans. This is mainly due to the increased risk associated with lending to individuals or businesses with limited financial resources or credit histories. The higher interest rates help compensate for the higher default risk and cover the administrative costs of providing these small loans.
However, microloans still offer more affordable rates compared to informal moneylenders or loan sharks, making them a more viable option for borrowers in need.
In addition to providing capital, many MFIs also offer other support services to borrowers. These services can include financial literacy training, business development advice, and mentorship programs. By combining financial resources with capacity-building initiatives, microfinance institutions aim to empower borrowers and improve their chances of success in their entrepreneurial endeavors.
Microloans have demonstrated their effectiveness in empowering individuals and communities by fostering economic growth and reducing poverty. Successful microloan programs have led to the creation of new businesses, increased employment opportunities, and improved living standards for borrowers and their families. As a result, microfinance has become a powerful tool for promoting inclusive economic development and addressing financial exclusion.
In conclusion, microloans provide a lifeline to individuals and small businesses that lack access to traditional forms of financing. By offering small loan amounts, simplified application processes, and additional support services, microfinance institutions enable borrowers to pursue their entrepreneurial dreams and improve their economic well-being. While microloans come with higher interest rates, they still represent a more affordable and sustainable option for borrowers who are often excluded from mainstream financial systems.
With continued support and expansion, microfinance has the potential to make a significant impact in the fight against poverty and inequality.